
A strained back muscle can be quite a nuisance and pain in everyday life, as it can limit a lot of our daily activities. Fortunately, we have quite a few measures that we can take in order to ease the pain and discomfort, and this includes back workouts and stretches for strength and recovery. This article will present to you a few simple but powerful strategies for easing the strain on your back muscles, along with treatment options and preventive approaches that you can take!
What is Back Muscle Strain?
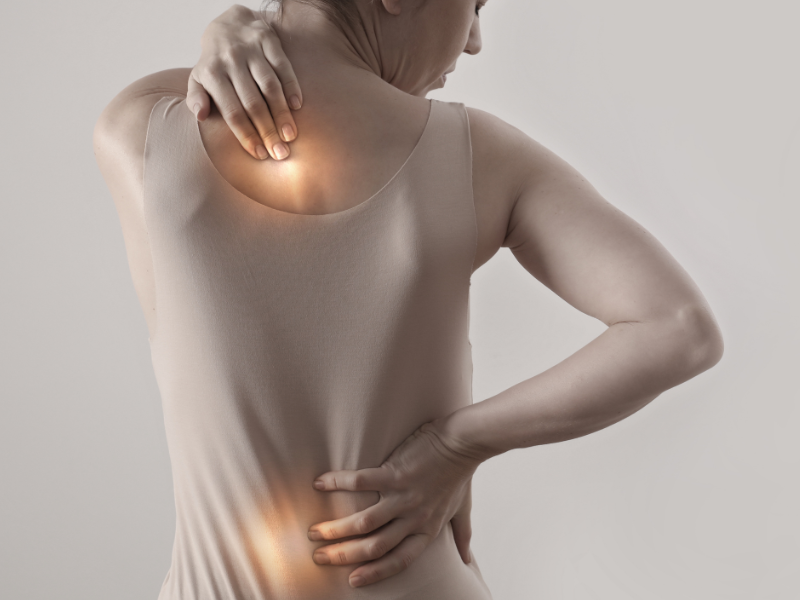
A back muscle strain is the result of the muscles in the back getting overstretched or torn due to overuse and any sudden movements.
Strains can also occur especially for athletes and people who experience whiplash. As the back relies on a group of muscles, tendons, and ligaments for support, these muscles need to be maintained with strength and flexibility to prevent strain and reduce pain.
Learn more about activating back muscles:
10 Best Lat Exercises For Building A Stronger Back
Vertical Pull Exercises: 4 Beginner-Friendly Movements To Try
Symptoms and Signs
Below are the symptoms to look out for in your body that would suggest that you’re suffering from muscle strain of some kind in your back [1].
- Pain that gets worse with movement (like bending, twisting, lifting, or walking)
- Muscle spasms (sudden, uncontrollable tightening of muscles)
- Difficulty standing or sitting up straight because of pain or stiffness
- Pain that might spread into the buttocks, but usually doesn’t go into the legs
- A popping or tearing feeling when the injury happens
- Swelling, bruising, severe pain, or inflammation in the affected area
- Muscle cramps that may happen whether you’re active or resting
- Pain that lasts up to 10-14 days, but could become chronic if it doesn’t heal properly
When to See a Doctor
If whatever pain you’re experiencing lasts more than a week and it doesn’t improve with rest, it’s best to consult a physical therapist or doctor. If the pain also spreads to one or both legs, and you’re feeling some weakness or tingling in the legs, it’s a sign to consult someone. Sudden weight loss and muscle spasms or muscle tension in the affected area are also signals your body might be sending for help.
Causes and Risk Factors
Causes for back muscle strain or pulled back muscle can be a result of anything from sudden movements like twisting or improper lifting to repetitive overuse. The lower back, also known as the lumbar region, is usually more prone to injuries as it supports most of the body weight and helps with everyday movements like twisting, bending forward, lifting, etc [2].
The risk factors for such a condition include age, lack of exercise, excess weight, and poor posture. You can also suffer from strains and pulled muscle if you have improper lifting techniques and weak abdominal muscles or core strength which increases the risk. Even psychological stress, smoking, and conditions like arthritis or herniated discs further contribute to back muscle strain.
You may also like:
Is It Better to Do Cardio Before or After Weights? Learn About Expert Opinions
8 Best Muscular Endurance Exercises for Lasting Strength and Stamina
Exercises and Stretches for Back Muscle Strain
Here are a list of exercises, stretches, and yoga poses you can try that’ll offer you some relief for back strain.
1. Reverse Dumbbell Fly:
Helps with: Shoulder and upper back muscles
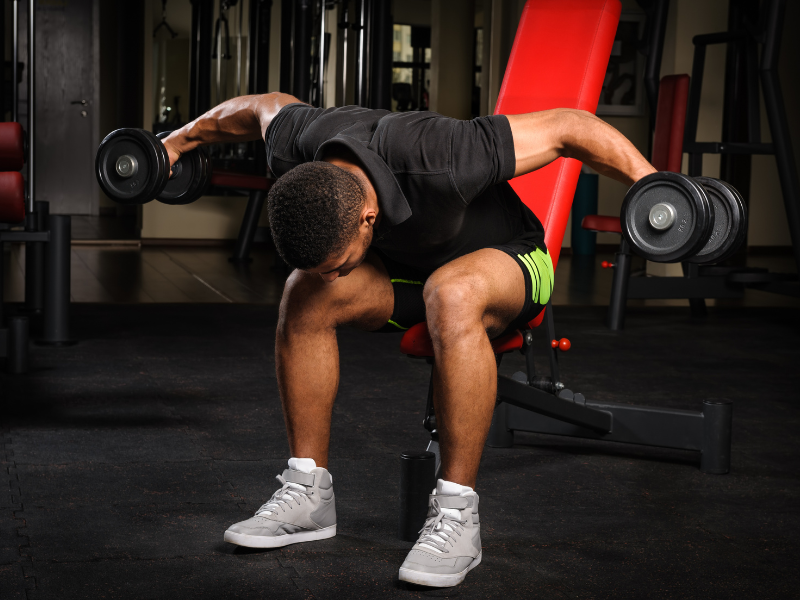

How to do:
- Stand with feet hip-width apart, holding a dumbbell in each hand, palms facing each other. Hinge at your hips with a slight bend in your knees, keeping your back straight.
- Bend your elbows slightly and raise your arms out to the sides, squeezing your shoulder blades together until your arms are level with your shoulders.
- Slowly lower the dumbbells back to the starting position, maintaining control throughout.
- Perform 8-12 reps for 2-3 sets.
2. Knees to Chest Pose
Helps with: Lower back muscles
How to do:
- Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor.
- Inhale, then exhale and bring your knees toward your chest, wrapping your arms around them.
- Gently pull your knees closer to your chest, keeping your back flat on the floor.
- Hold for 20-30 seconds, breathing deeply.
- Release and return to the starting position.
3. Shoulder Rolls
Helps with: Shoulder and upper back muscles
How to do:
- Stand or sit up straight with your arms relaxed by your sides.
- Inhale as you lift your shoulders towards your ears.
- Exhale as you roll your shoulders back and down, squeezing your shoulder blades together.
- Repeat the roll for 10-15 reps in one direction, then switch to rolling forward.
4. Cat-Cow Pose
Helps with: Mid and lower back muscles
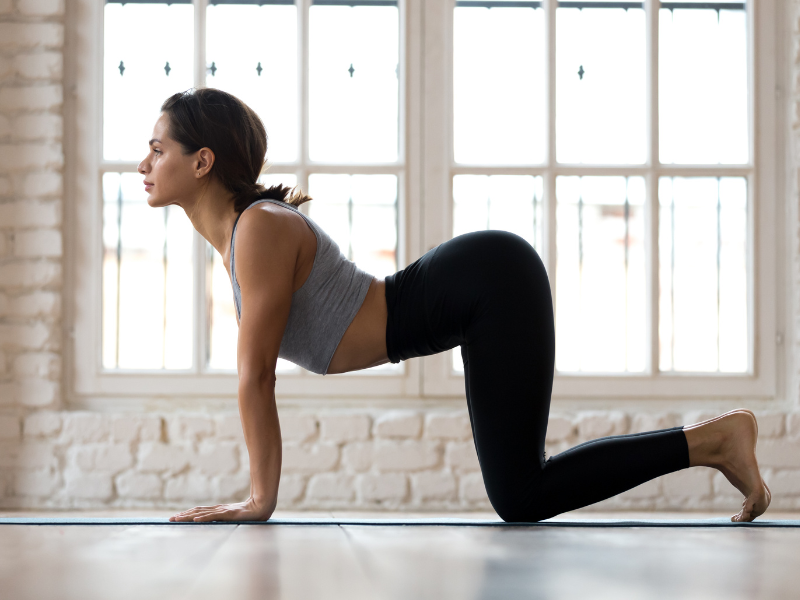

How to do:
- Start on all fours with wrists under shoulders and knees under hips.
- Cat Pose: Exhale and round your spine, tucking your chin to your chest.
- Cow Pose: Inhale, arch your back, lifting your chest and tailbone, and look forward.
- Flow between both poses, synchronizing breath with movement.
- Perform for 8-12 breaths.
5. Glute Bridges
Helps with: Lower back muscles
How to do:
- Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart.
- Place your arms by your sides for stability.
- Inhale, then as you exhale, press through your heels and lift your hips toward the ceiling, squeezing your glutes at the top.
- Hold for a moment, then lower your hips back down slowly.
- Repeat for 10-15 reps.
6. Face Pull
Helps with: Upper back muscles
How to do:
- Attach a rope or resistance band to a high pulley or anchor point.
- Stand facing the anchor with feet shoulder-width apart and hold the rope or band with both hands, palms facing inward.
- Pull the rope towards your face, keeping your elbows high and flaring out to the sides. Squeeze your shoulder blades together as you pull.
- Slowly return to the starting position with control.
- Perform 10-15 reps.
Back workouts and exercises to try:
5-Minute Back Workout For Beginners
Treatment and Management
There’s a two-phase approach you can take to manage back muscle strain. Begin with treating the pain and muscle spasms with rest, ice packs, compression, and NSAIDs like ibuprofen [3]. But you should also avoid extended bed rest as it can lead to muscle weakness and stiffness. You should see some change in 24-48 hours as gradual movement and normal activities also aid in recovery, and within two weeks there will be a visible improvement.
However, if pain persists it’s time for physical therapy. This includes gentle massage, stretching, pelvic traction, or even electrical muscle stimulation to improve muscle strength and flexibility. Other alternative treatments you can try for relief include acupuncture, chiropractic care, and yoga. You can also use muscle relaxants and prescribed medications to help with managing the pain. In terms of preventive measures, use ergonomic support, practice regular exercise, check your posture, and maintain a healthy weight in order to reduce risks in the future.
You may also like: Top 8 Yoga Positions to Relieve Gas and Enhance Digestive Comfort
Conclusion
We hope that this article has helped you gain a better understanding of how to take care of your body when you’re suffering from this common issue. For more workout tips and resources to help you with your fitness journey, check out the JustFit app!





