


We’ve all faced stomach issues at some point, whether it’s diarrhea, constipation, or just general indigestion, and we each have our favorite remedies to tackle them. From DIY fixes to prescribed medicines, we’ve tried it all to manage symptoms of acute diarrhea and other stomach issues.
Enter the BRAT diet—often touted as a solution to these digestive issues. But what’s the scoop on the BRAT diet, and does it really live up to the hype? We’re here to dive into all the details and clear up any questions you might have about this intriguing dietary approach!
What is the BRAT diet
The term BRAT is an acronym for the four foods it emphasizes: bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast.
This diet is designed to address gastrointestinal issues by avoiding heavy foods and strong flavors while eating bland foods that are easy to digest.
Origins of the BRAT diet
If the foods in the BRAT acronym sound familiar from what you’ve seen fed to babies, you’re on the right track. The BRAT diet originally emerged as a meal plan recommended by pediatricians for young children experiencing stomach issues such as the flu or diarrhea [1].
It was designed as a temporary solution to help alleviate symptoms, treat diarrhea, and promote recovery through easy-to-digest foods.
How does the BRAT diet work?
It is based on the simple idea that mild foods can soothe the digestive system, especially after a stomach bug.
When experiencing diarrhea, the binding foods included in this diet—such as bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast—can help firm up the stool. These foods are bland, low in fiber, and gentle on the digestive tract, which can prevent further irritation.
This diet can not only help control the amount of stool produced but also ease stomach problems. Additionally, these easy-to-digest foods help suppress nausea and vomiting, making it easier to retain nutrients and promote a quicker recovery from stomach illness.
Is the BRAT diet recommended for adults?
While the BRAT diet has traditionally been recommended for children, it has also proven beneficial for adults.
This diet consists of high-starch, low-fiber foods that help firm up stools for both adults and children. Foods like bananas play a key role in this process by supporting stool formation and replacing nutrients like potassium lost through vomiting and diarrhea.
Overall, the BRAT diet serves as a quick, gentle solution that helps retain vital nutrients and provides relief during digestive distress, and can be supplemented with other bland foods.

How to follow the BRAT diet
The BRAT diet can be followed in flexible variations, but a 3-day approach is the most common one recommended by medical professionals to treat diarrhea.
The first six hours
After you’ve stopped vomiting, your stomach will need some time to rest. So for the next hour or two, it would be best to just have something refreshing that would also prevent nausea and soothe your stomach flu, such as hard candy or popsicles that shouldn’t be chewed on. If the nausea continues, move on to having some sips of water or ice chips.
Day One
It is crucial to focus on hydration for the first 24 hours. Begin by sipping clear liquids at ten-minute intervals. Options include water, tea, apple juice, broths, clear soups, and electrolyte beverages. If nausea and vomiting symptoms return, restart the process by allowing your stomach to rest for an hour or two before coming back to hydration.
Day Two
You can begin to slowly introduce the four BRAT foods along with other recommended bland, low-fat, and low-fiber foods. These should be eaten in small portions every few hours. For specific suggestions on what to include in your diet, refer to the list below.
Day Three
If your condition has improved and you are no longer experiencing nausea or other symptoms, you can gradually resume your regular diet. However, if symptoms persist, continue to stick with the bland foods recommended by the BRAT diet.
“The BRAT diet should be individualized based on the severity of your digestive symptoms and how long you’ve been on it. As your symptoms improve, it’s helpful to re-introduce one new food at a time to assess your tolerance to it before you add new foods. This way, you can quickly determine which foods may be triggering your symptoms, and not avoid foods unnecessarily.”- Melissa Mitri, MS RD
Food suggestions to follow the BRAT diet

A bland diet doesn’t have to be boring; it simply involves foods that are gentle on the stomach. While the BRAT diet focuses on bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast, the key is to choose binding foods that help firm up stools.
It is also important to avoid spicy foods, as they can further irritate the digestive system [2]. Here are some other bland foods and drink options you can consider:
Solid foods:
- oatmeal and cooked cereals
- sweet potatoes and boiled or baked potatoes
- plain pasta and noodles
- Soft fruits that include avocado, melons, and pumpkin
- Cooked vegetables, steamed or boiled, like beans, carrots, squash, zucchinis, beats, and mushrooms
- steamed, grilled, or baked tender meats like chicken and turkey.
- boiled eggs and tofu
- saltine crackers and pretzels
- puddings and custard
Beverages
- Vegetable broths and clear broths
- plant-based milk such as almond milk, walnut milk, coconut milk, and flax milk
- apple juice, coconut water, flat soda, and weak tea
- sports drinks or other beverages with electrolytes
- Homemade solution to prevent dehydration: Take 1 liter of clean or warm water and mix it with 1/2 teaspoon of salt and 6 teaspoons of sugar. Stir it well until the salt and sugar dissolve in the liquid completely. Cool the drink to your desired temperature before consuming it.
Foods to avoid in the BRAT diet
The types of foods that are meant to be avoided in this diet plan include those that can further irritate your digestive system.
Therefore, it calls for abstaining from foods that are high in sugar and fat, as well as those that are spicy or contain dairy. Following are some food items to take note of:
- Milk and dairy products like cheese, ice cream and full-fat milk
- Meat like veal, salmon, sardines, pork, and steak.
- Raw vegetables that include sauerkraut, salad greens, onions, parsnips, and corn on the cob
- Acidic and citrus fruits like pineapples, oranges, lemons, and grapes, along with berries, raisins, figs, currants, and unpasteurized juices
- Anything fried, fatty or spicy
- Alcohol and caffeinated beverages
Is the BRAT diet effective?

It’s important to clarify that the BRAT diet is not intended for weight loss but rather for managing illnesses such as acute diarrhea, stomach flu, and vomiting.
It can also be used post-surgery when gentle foods are needed for digestion [3]. Healthcare providers have historically recommended this diet to help parents manage acute gastroenteritis in children [4].
However, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) no longer endorses this diet. They have found that it can be overly restrictive and may lead to nutritional deficiencies due to its lack of essential micronutrients, macronutrients, and adequate protein.
Instead, the AAP recommends transitioning to a more balanced diet for children and full-strength formula for infants once they start recovering. For adults, while the BRAT diet can help soothe the stomach, it is advisable to return to a regular meal plan soon to avoid nutritional and calorie deficiencies.
Although studies show that BRAT foods can provide relief from diarrhea and other stomach issues, this diet is best viewed as a short-term solution for immediate discomfort rather than a long-term approach. The restrictive nature of the BRAT diet can lead to nutrient deficiencies, making it unsuitable for prolonged use.

Alternative treatments for diarrhea
The most obvious step to take is to avoid certain foods that can make symptoms worse. Although the BRAT diet shouldn’t be followed for too long, it is best to avoid greasy and spicy food for a few days, along with alcohol and caffeinated drinks.
To start the healing process, anti-diarrheal medications can be helpful, and over-the-counter options are available online. However, these medications may not be effective if your stomach issues are caused by bacteria, parasites, or other underlying medical conditions.
Always consult with a medical professional before taking medication, especially for children. This ensures it is appropriate and safe for your specific situation.
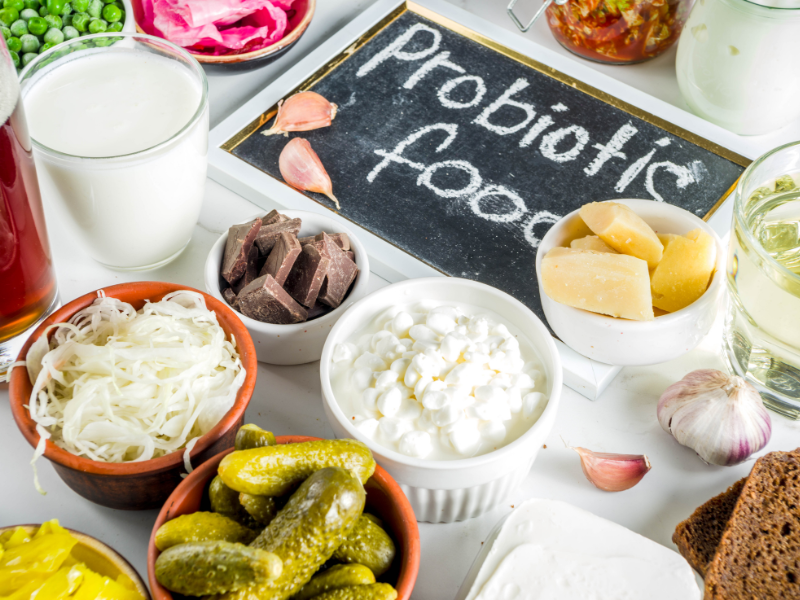

Importance of probiotic foods and supplements for diarrhea
Incorporating probiotic foods and supplements into your diet can help speed up the healing process. Research indicates that strains like Lactobacillus GG and Saccharomyces boulardii can reduce the duration of stomach illnesses by about one day, making them particularly effective for managing diarrhea.
Probiotics are available in both liquid and capsule forms and can also be found in fermented foods such as kombucha and yogurt. However, it’s important to avoid excessive dairy consumption, as it can sometimes make the diarrhea worse.
Last, but certainly not the last, during this whole process the body is at great risk of dehydration. So it is essential to keep hydrating yourself through it all.
When to seek help
While the BRAT diet can help alleviate digestive discomfort and speed up recovery at home, some cases may require medical attention. If you experience any of the following symptoms, consult a doctor as soon as possible:
- Excessive thirst and dry mouth
- Reduction in urine
- Dizziness and severe weakness
- A temperature at or above 102ºF
- Rectal pain or bleeding
- If your illness continues for more than three days without signs of improvement
Soluble fiber can also slow down diarrhea as it absorbs water in the digestive tract, making stool firmer and slowing its passage [6].”

Conclusion
To summarize, the BRAT diet was once widely recommended by physicians and pediatricians for managing children’s stomach illnesses. Its bland, low-fiber, low-protein, and low-fat food can help ease nausea and support recovery from vomiting and diarrhea.
However, due to its lack of essential nutrients, it is not suitable for long-term use, as it may lead to nutrient and calorie deficiencies. Therefore, it should be followed with caution and on a very short-term basis.
It is important to transition back to a normal diet to avoid deficiencies and ensure a balanced intake of essential nutrients. For those seeking guidance on following a more nutritious diet and healthier lifestyle, check out the JustFit app!
What can you eat on a BRAT diet?
Are eggs ok on the BRAT diet?
How does the BRAT diet work?
How many days should you do the BRAT diet for diarrhea?
Why is the BRAT diet not recommended for diarrhea?
Brat diet. Oregon Clinic. (2023, December 7). Available from: https://www.oregonclinic.com/resource/diets-brat/
Churgay, C. A., & Aftab, Z. (2012, June 1). Gastroenteritis in children: Part II. prevention and management. American Family Physician. Available from: https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2012/0601/p1066.html
Department of Health & Human Services. (2002, November 6). Diarrhoea. Better Health Channel. Available from: https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/diarrhoea
Erdogan, A., Rao, S. S., Thiruvaiyaru, D., Lee, Y. Y., Coss Adame, E., Valestin, J., & O'Banion, M. (2016). Randomized clinical trial: mixed soluble/insoluble fibre vs. psyllium for chronic constipation. Alimentary pharmacology & therapeutics, 44(1), 35–44. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.13647
Fiber. Mount Sinai Health System. (n.d.). Available from: https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/supplement/fiber#:~:text=Fiber%20can%20be%20used%20to,firmer%20and%20slower%20to%20pass
Guarino, A., Guandalini, S., & Lo Vecchio, A. (2015). Probiotics for Prevention and Treatment of Diarrhea. Journal of clinical gastroenterology, 49 Suppl 1, S37–S45. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0000000000000349
Nazarian, L. F. (1997, July 1). A synopsis of the American Academy of Pediatrics’practice parameter on the management of acute gastroenteritis in young children | pediatrics in review | American Academy of Pediatrics. A Synopsis of the American Academy of Pediatrics’ Practice Parameter on the Management of Acute Gastroenteritis in Young Children. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1542/pir.18-7-221
Treating diarrhea in children – is the brat diet best?. Pediatric Specialists of Plano. (2019, September 30). Available from: https://www.psopkids.com/treating-diarrhea-in-children-is-the-brat-diet-best/
University Hospitals. (2022, June 23). Spicy food challenges: Harmful or healthy?. University Hospitals. Available from: https://www.uhhospitals.org/blog/articles/2022/06/spicy-food-challenges-harmful-or-healthy#:~:text=Increased%20production%20of%20mucus%20in,Painful%20bowel%20movements.
Vankoot, B. (2019, August 19). Foods that bind the bowels | livestrong. LIVESTRONG.COM. Available from: https://www.livestrong.com/article/449981-foods-that-bind-the-bowels/
Weir, S.-B. S., & Akhondi, H. (2023, July 25). Bland diet. StatPearls [Internet]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538142/#





